Operations Management in the Fashion Industry
Operations Management (OM) is a crucial part of any supply chain, which is dedicated to managing the product and the delivery process of products and services. It embodies the capabilities of an enterprise, which influence its future development directions and strategic choices. The focus of most operations directors has shifted from planning and control to enhancement and optimization. Additionally, the same authors pointed out that enterprises operating in various ways need to continuously improve their operations to maintain their competitive advantages over competitors.
In the retail industry, especially in the fashion field, OM involves analyzing, understanding, and potentially improving the processes of each part of the chain, from distribution centers to stores, including transportation and other distribution adjustments. When analyzing the literature, the focus is often on Store Operations (SO) because academic research shows that the operation and management of retail stores is one of the most significant challenges in the retail supply chain. In fact, even with correct planning, poor store operations can lead to unfavorable results. Moreover, the optimization of store operations is an essential factor for success in the retail sector. However, there is a lack of publications focusing on store-level operations, so there is a certain research gap in this area.
Operations management refers to the management of business practices to achieve the highest possible operational efficiency and effectiveness within an enterprise. It focuses on how to transform resources such as equipment and labor into goods and services as efficiently as possible to maximize corporate profits. Operations management pursues the highest possible net operating profit by balancing costs and profits.
The operations management of the fashion industry consists of the following aspects:
Product Design
This strategic decision area covers the design of all fashion products. The goal of operations management is to ensure that product design aligns with the organizational capabilities and business strategies of the enterprise. In the current market environment, each brand usually focuses on designs based on advanced technologies and current consumer demand preferences to meet the diverse and personalized needs of the fashion market.
Quality Management
Any brand should place a high emphasis on quality in its production processes and products. The objective of this strategic decision area is to meet consumers’ expectations of product quality. Enterprises ensure product quality by formulating and implementing high-quality standards for sports shoes, clothing, and outerwear products, and implementing Total Quality Management (TQM), thereby enhancing brand image and consumer satisfaction.
Process and Capacity Design
In this strategic decision area, operations management must prioritize the simplification and effectiveness of the product production process to ensure the delivery of acceptable, efficient, and high-quality products. In the fashion industry, operations directors usually adopt continuous improvement strategies to adjust and optimize the company’s product strategies and production requirements according to the dynamic changes in market demand, so as to maintain the competitiveness of the enterprise.
Supply Chain Management
Any fashion brand should establish an excellent supply chain operation system, which is crucial for effectively supporting the global sports shoes, clothing, and other related businesses. In this strategic decision area of operations management, the ideal state is to align the supply chain with the overall strategic objectives of the company. Enterprises achieve this goal by automating and intelligentizing the supply chain, optimizing supplier selection, product distribution, distributor management, and the transportation distances between retailers, thereby improving the efficiency and flexibility of the supply chain.
Inventory Management
The main objective of this strategic decision area is to maintain effective operations management, minimize inventory costs to the greatest extent possible, and improve the effectiveness and operational efficiency of inventory. Managers usually adopt the perpetual inventory management method, which involves continuously monitoring inventory levels and ensuring that inventory can be timely and accurately transferred from the supply chain to distributors and retailers to meet market demand and avoid inventory overstock or stockouts.
Scheduling
Scheduling mainly focuses on the coordination and cooperation between the company’s internal operations and the supply chain, distribution, and retail operations. In the strategic decision area of operations management, its goal is to maximize the utilization rate of enterprise resources, ensure the efficient operation of each link, and thereby improve the overall operational efficiency.
Design Decisions
This requires an in-depth understanding of consumers’ selection behaviors and preferences among product series. Retailers like Zara are good at grasping market trends by studying best-selling products instead of relying solely on traditional and relatively conservative design concepts. They can 敏锐地 capture the current fashion trends and respond quickly, without being restricted by traditional seasonal spring and autumn product designs, thereby better meeting the changing needs of consumers.
Procurement Decisions
Procurement decisions need to effectively manage the risks of over-ordering or under-ordering compared to market demand. For companies with shorter delivery times, a multiple-purchase model can be adopted, and during peak demand periods, early demand information can be used to increase production to meet market demand while avoiding inventory overstock or stockout risks.
Distribution Decisions
Once the product design and its production quantity are determined, reasonable distribution decisions must be made to ensure that inventory is correctly allocated within the store network. Taking Zara as an example, its distribution model focuses on the optimization of store display. If a product lacks the main size items in a certain store, the item will be removed from the store’s inventory. This requires that distribution decisions should fully consider the timely allocation of scarce inventory to other stores in the network to always maintain the correct size combination on display. Doing so can increase sales by up to 4%.
Strategies for Reducing High Production Costs
Generally, enterprises can reduce production costs through reasonable production planning and effective operations scheduling, thereby optimizing the available resources within the production facilities. To this end, it is recommended that enterprises implement an appropriate aggregate production planning process to minimize the total costs related to labor and inventory levels in the medium term. In the short term, scheduling techniques must be applied to allocate production tasks to the resources of clothing manufacturing plants to reduce time wastage in assembly and setup operations. In the design process of required resources (such as manufacturing modules, setup personnel, floor space, machinery, and equipment), the use of simulation technology has been proven to minimize the total production cost in different production scenarios.
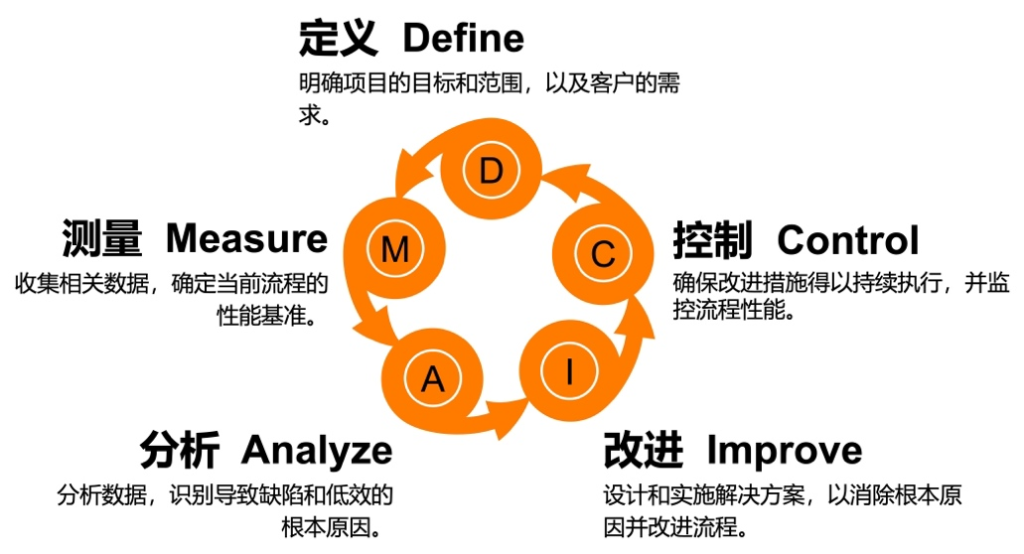
Similarly, technologies such as RFID and cloud computing can be used to capture and monitor real-time production information, thereby providing production scheduling solutions based on intelligent optimization techniques such as heuristic and meta-heuristic algorithms. Production systems that support lean manufacturing are also excellent options for reducing costs and improving product quality, facilitating the implementation of tools and methods such as 5S, DMAIC, Kaizen, SMED, and TPM, as well as the application of Six Sigma management methods. On the other hand, under the global supply chain model, it is necessary for enterprises to consider the global procurement of materials and production services to obtain products and services with the flexibility and speed required by the market. Therefore, textile and apparel enterprises can focus on their own value-added production processes and outsource processes in which they lack sufficient competitiveness. For textile and apparel enterprises that need to purchase materials from suppliers, it is recommended to implement a Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system to reduce excessive raw material inventory, ensure on-time supply, and avoid cost overruns and production delays.
Conclusion
Operations management helps to solve the problems related to low sales levels, low turnover rates, excessive inventory, and high production costs in the fashion industry, thereby improving the productivity and competitiveness of enterprises. Operations management provides enterprises with strategies for promoting supply chain integration, appropriate demand forecasting methods, Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) methods, lean manufacturing principles, the application of information technology, and long-term, medium-term, and short-term production planning techniques, helping enterprises gain an advantage in the fierce market competition.